

Has already exceeded 3.8GW as of 2011.Advances in foundation technology and growing turbine size are beginning to push the boundaries of offshore wind power development to deeper waters where high quality wind resource is abundant.The recent success of world ’s ?rst ?oating wind turbine demonstration by Statoil has evoked new perspectives in the offshore wind industry and greater interest in ?oating wind power.Besides,increased productivity,lesser environmental,aesthetic and acoustic require-ments are added incentives for deep water wind development.In an attempt to reduce the overall cost of wind energy,countries endowed with deep water coastlines (most of Western Europe,Japan and USA)are currently exploring the feasibility of ?oating windmills. Offshore wind development has witnessed a steady growth in the last decade.Europe leads the developments with the majority of offshore wind farms set-up in areas combining high windiness and shallow waters.According to the European Wind Energy Association ,the cumulative installed capacity of these plants

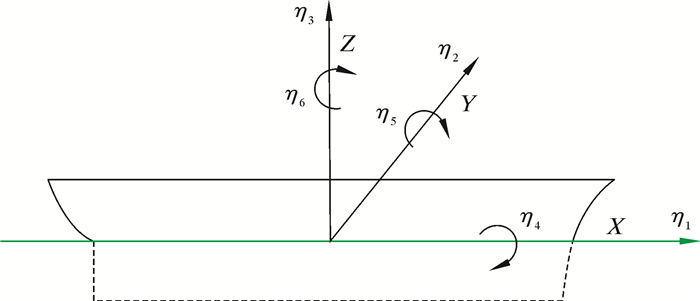
The hydrodynamic responses of a ?oating spar wind turbine under regular and irregular waves are measured by experimental techniques and the results are validated using the industry standard time-domain modelling tool,OrcaFlex.A 1:100scale model is built with four mooring lines and tested in a wave tank for various wave conditions.The surge,heave and pitch motions of the spar model are measured using an optical tracking system both at its centre of mass and nacelle locations.The same motions are also simulated numerically using OrcaFlex under identical wave conditions.The measured hydrodynamic responses are evaluated as Response Amplitude Operator (RAO)and compared with numerical simulations.The results show a very good agreement in RAO between the experiments and numerical parison with existing literature for similar spar con ?guration indicates that the present study better captures the non-linearities from the mooring lines and the four-point mooring con ?guration is found to offer signi ?cant reduction in surge motions.įloating wind turbines are a promising new technology in the ?eld of offshore wind power development.In recent years,signif-icant R&D effort has been spent in conceiving ?oater designs that are stiff enough to accommodate wind turbines and stable enough to cope with the highly dynamic environments that prevail in deep seas.Concomitantly,great amount of time has also been invested in developing design tools to accurately model and predict the dynamics of coupling wind turbines to ?oating structures.Yet,the move towards commercialisation of the technology has rather been protracted.As with any new technology,large scale development requires extensive model testing and demonstration to establish credibility on a concept.An important ?rst step to this is perfor-mance veri ?cation by laboratory scale testing and validation of design tools as most design ?aws can be identi ?ed at a lesser expense. Institute for Energy Systems,School of Engineering,The University of Edinburgh,The King ’s Buildings,Edinburgh EH93JL,UKĪvailable online 23November 2012Keywords: Hydrodynamic response of a stepped-spar ?oating wind turbine:Numerical modelling and tank testing


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
